Disulfide Bond Analysis Service
Disulfide bond (S-S bond) is formed by oxidation of the sulfhydryl group (-SH) on two cysteines in the protein. It is an important post-translational modification of protein. Disulfide bond is essential for protein molecules to maintain the correct advanced structure and maintain protein bioactivity. The distribution of disulfide bonds in antibody drugs is a direct structural characteristic of the drugs. Therefore, confirmation of disulfide bonds plays a very important role in the confirmation process of antibody drug structure. MtoZ Biolabs has developed a high-resolution mass spectrometry, coupled with pLink-SS software, to provide our customers with accurate analysis of disulfide bonds and free cysteines. Our sample preparation steps have also been optimized to prevent in vitro exchange of disulfide bonds, and maintain native structure.
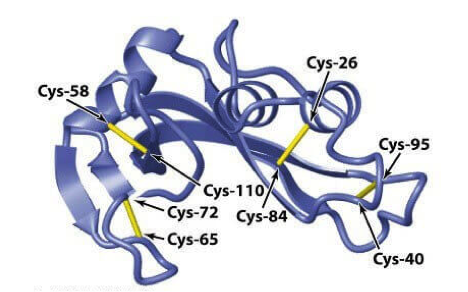
Figure 1. Disulfide Bond Analysis of Biopharmaceuticals
Applications
1. Identification of the Number of Disulfide Bonds in the Biopharmaceuticals and Free Cysteines
2. Identification of the Position of Disulfide Bonds in the Biopharmaceuticals
Deliverables
1. Experiment Procedures
2. Parameters of Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometer
3. MS Raw Data Files
4. Disulfide Bonds and Free Cysteines Analysis Results
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
Related Services
Identification of Biopharm
Variation Analysis
Purity Analysis
How to order?



